Nonlinear curve fitting with confidence intervals
Posted February 18, 2013 at 09:00 AM | categories: data analysis | tags:
Updated February 27, 2013 at 02:41 PM
Our goal is to fit this equation to data \(y = c1 exp(-x) + c2*x\) and compute the confidence intervals on the parameters.
This is actually could be a linear regression problem, but it is convenient to illustrate the use the nonlinear fitting routine because it makes it easy to get confidence intervals for comparison. The basic idea is to use the covariance matrix returned from the nonlinear fitting routine to estimate the student-t corrected confidence interval.
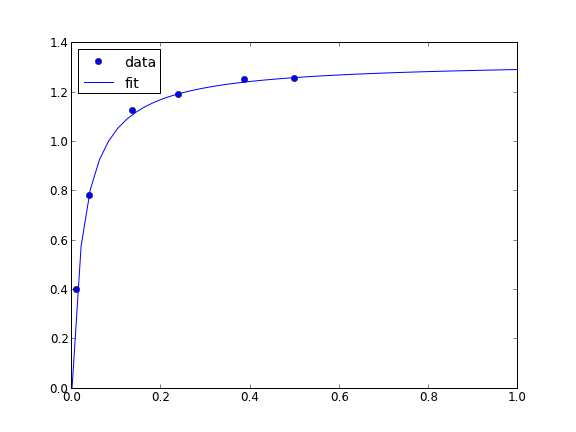
# Nonlinear curve fit with confidence interval import numpy as np from scipy.optimize import curve_fit from scipy.stats.distributions import t x = np.array([ 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1. ]) y = np.array([ 4.70192769, 4.46826356, 4.57021389, 4.29240134, 3.88155125, 3.78382253, 3.65454727, 3.86379487, 4.16428541, 4.06079909]) # this is the function we want to fit to our data def func(x,c0, c1): return c0 * np.exp(-x) + c1*x pars, pcov = curve_fit(func, x, y, p0=[4.96, 2.11]) alpha = 0.05 # 95% confidence interval n = len(y) # number of data points p = len(pars) # number of parameters dof = max(0, n-p) # number of degrees of freedom tval = t.ppf(1.0 - alpha / 2.0, dof) # student-t value for the dof and confidence level for i, p,var in zip(range(n), pars, np.diag(pcov)): sigma = var**0.5 print 'c{0}: {1} [{2} {3}]'.format(i, p, p - sigma*tval, p + sigma*tval) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot(x,y,'bo ') xfit = np.linspace(0,1) yfit = func(xfit, pars[0], pars[1]) plt.plot(xfit,yfit,'b-') plt.legend(['data','fit'],loc='best') plt.savefig('images/nonlin-fit-ci.png')
c0: 4.96713966439 [4.62674476567 5.30753456311] c1: 2.10995112628 [1.76711622427 2.45278602828]
Copyright (C) 2013 by John Kitchin. See the License for information about copying.