Nonlinear curve fitting by direct least squares minimization
Posted February 18, 2013 at 09:00 AM | categories: data analysis | tags:
Updated February 27, 2013 at 02:40 PM
Here is an example of fitting a nonlinear function to data by direct minimization of the summed squared error.
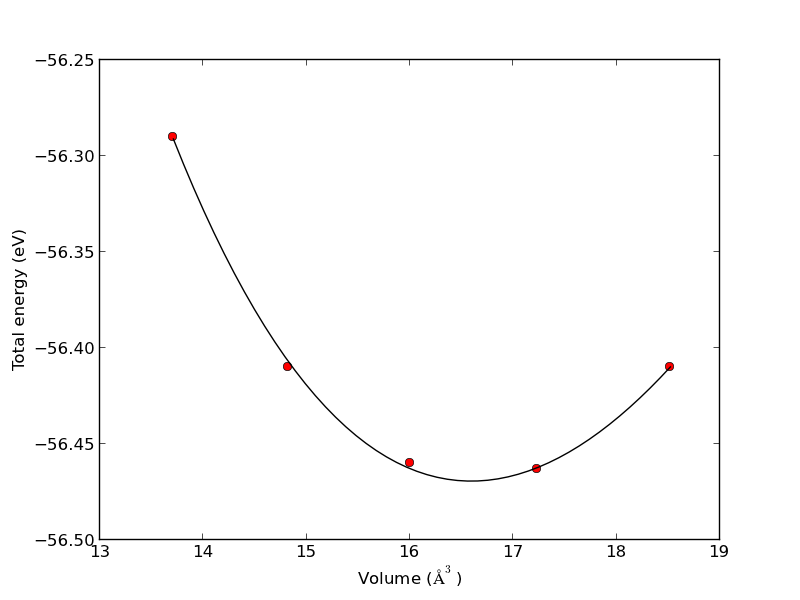
from scipy.optimize import fmin import numpy as np volumes = np.array([13.71, 14.82, 16.0, 17.23, 18.52]) energies = np.array([-56.29, -56.41, -56.46, -56.463,-56.41]) def Murnaghan(parameters,vol): 'From PRB 28,5480 (1983' E0 = parameters[0] B0 = parameters[1] BP = parameters[2] V0 = parameters[3] E = E0 + B0*vol/BP*(((V0/vol)**BP)/(BP-1)+1) - V0*B0/(BP-1.) return E def objective(pars,vol): #we will minimize this function err = energies - Murnaghan(pars,vol) return np.sum(err**2) #we return the summed squared error directly x0 = [ -56., 0.54, 2., 16.5] #initial guess of parameters plsq = fmin(objective,x0,args=(volumes,)) #note args is a tuple print 'parameters = {0}'.format(plsq) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot(volumes,energies,'ro') #plot the fitted curve on top x = np.linspace(min(volumes),max(volumes),50) y = Murnaghan(plsq,x) plt.plot(x,y,'k-') plt.xlabel('Volume ($\AA^3$)') plt.ylabel('Total energy (eV)') plt.savefig('images/nonlinear-fitting-lsq.png')
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000020
Iterations: 137
Function evaluations: 240
parameters = [-56.46932645 0.59141447 1.9044796 16.59341303]
Copyright (C) 2013 by John Kitchin. See the License for information about copying.